Centre for Advanced Studies on Climate Change
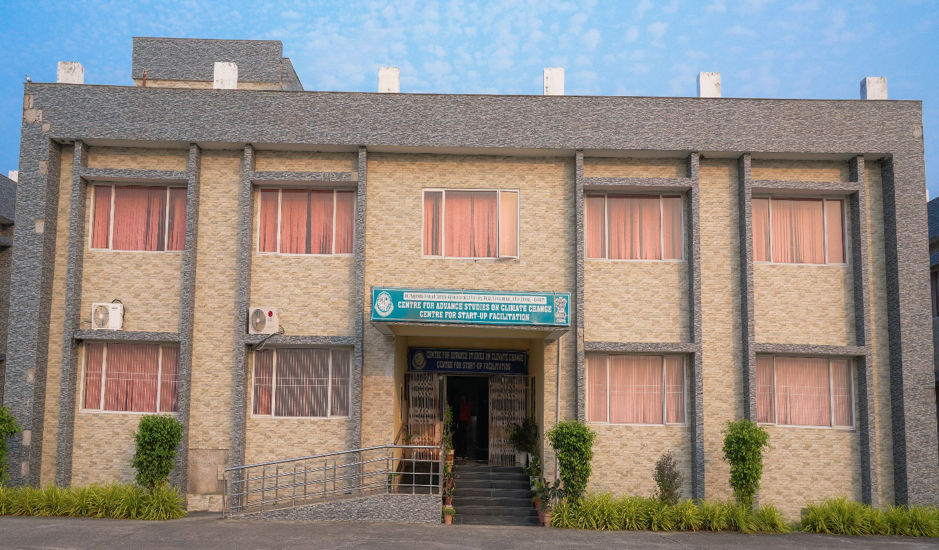



Name of Centre of Excellence: – Centre for Advanced Studies on Climate Change
Vision & Mission
- To excel as knowledge- and technology-driven enterprise in the field of climate change and Climate Resilient Agriculture aimed at delivering socio-economic benefits to the farmers and society.
- To enhance resilience and productivity of crops through resource-efficient sustainable technologies; develop climate-smart crops and cropping systems; achieve net-zero water exploitation; sustain the soil health and minimize the risk of nutrients loss.
Thrust Areas
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture and Crop Improvement
Development and evaluation of climate-resilient crop varieties, cropping systems, and production technologies suitable for diverse agro-ecological conditions. - Climate Change Impact Assessment and Modeling
Study of crop–weather relationships, simulation modeling, and climate change projections to design effective mitigation and adaptation strategies for agriculture. - Resource-Efficient and Sustainable Intensification
Promotion of technologies for sustainable intensification, soil health management, nutrient-use efficiency, and net-zero groundwater exploitation. - Agroclimatic Resources Assessment
Development of comprehensive climate and water databases, assessment of climate impacts on water resources, and implementation of water conservation and budgeting. - Biotic and Abiotic Stress Management
Exploration of genetic diversity for stress tolerance and development of technologies to manage emerging pest and disease challenges under changing climate. - Climate-Smart Technology Development and Demonstration
Design, validation, and dissemination of climate-smart agricultural practices for enhancing farm productivity and climate resilience. - Early Warning Systems and Advisory Services
Development of pest outbreak models, climate-based risk forecasting, and delivery of actionable weather-based advisories for farmers. - Capacity Building and Skill Development
Strengthening the adaptive capacity of farmers and rural communities through training, demonstrations, and knowledge dissemination on climate-resilient and climate-smart agriculture. - Habitat Sustainability and Waste Recycling
Promotion of sustainable waste management, recycling, and resource conservation practices for ecological balance.
Goals
To develop and promote climate-resilient, resource-efficient, and sustainable agricultural systems that safeguard food and nutritional security, enhance farmers’ income, conserve natural resources, and strengthen the adaptive capacity of farming communities in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Objectives
- To evaluate agroclimatic resources for implementing location-specific agriculture under changing climatic conditions.
- To study crop-weather relationships, simulation modeling, and climate change impacts for effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
- To explore the genetic diversity of major crops for resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses under changing climatic scenarios at physiological, biochemical, and molecular levels.
- To enhance the system productivity of various cropping systems in response to changing climatic conditions.
- To achieve habitat sustainability through waste recycling and management.
- To develop pest outbreak models and early warning systems to support prevention and rapid response to both emerging and existing pests.
- To provide actionable weather-based advisories to farmers for mitigating climate risks and enhancing farm profitability.
- To improve the adaptive capacity of rural communities to climate change through demonstrations and training on climate-resilient and climate-smart agricultural interventions.
The Centre for Advanced Studies on Climate Change has emerged as a pivotal institution in promoting climate-smart farming systems and Agrometeorological Research and Applications across Bihar. The Centre has successfully demonstrated scalable and impactful interventions that have strengthened climate resilience, resource-use efficiency, and farmer livelihoods.
-
Climate Resilient Agriculture (CRA) Programme
Large-scale Implementation and Outreach
- 15,834 acres brought under climate-resilient practices.
- 75,000 farmers benefitted across 13 districts and 65 CRA villages.
- Weekly advisories delivered to 6.5 lakh farmers.
Significant Gains in Productivity, Profitability, and Resource Efficiency
- Productivity increased by 14–22% across major crops.
- Profitability enhanced by 16–35%, improving farm incomes substantially.
- Cropping intensity jumped from 144% to an impressive 275%.
- Irrigation cost reduced by 30%, with average irrigations dropping from 5 to 3.
- Fertilizer consumption reduced by 38% through precision nutrient tools.
Breakthrough Improvements in Major Cropping Systems
- 62.4% increase in rice–wheat system productivity through timely sowing and assured irrigation.
- Best performing systems identified:
- Rice–Potato+Maize
- Rice–Potato–Mung bean
- Maize–Wheat–Mung bean
Transformative Adoption of Climate-Smart Technologies
Massive increase in adoption of resource-conserving technologies:
- Happy Seeder: 100% increase
- Leaf Colour Chart (LCC): 83% increase
- Raised Bed Planter: 85% increase
- Zero Tillage: 66.66% increase
- Laser Land Leveling: 40% increase
- Tractor usage: 90% increase
Custom hiring centers equipped with 279 machines, ensuring timely operations.
Proven Success in Key Interventions
Direct Seeded Rice (DSR)
- 7–14 days earlier sowing
- 40% labour savings
- 20–25% water saving (up to 50% in some cases)
- Cost reduction of Rs. 10,000/ha
- Higher net income of Rs. 8,000–10,000/ha
Zero Tillage
- Wheat: 16.12% higher yield (43.22 q/ha vs 37.21 q/ha)
- Lentil: 12.72% higher yield
- Mung bean: 31.21% higher yield
- Saves Rs. 15,000/ha in production cost
- Reduces 1.5 Mg CO₂-eq/ha/season
Raised Bed Planting
- Maize: 22.09% higher yield
- Mustard: 27.65% higher yield
- Wheat: 16.36% higher yield
- Uses 30% less water; enables crop diversification
Precision Nutrient Management (LCC/NE/Green Seeker)
- 20.10% higher rice yield
- 38% reduction in fertilizer use and cost
Other Achievements
- Intercropping Maize + Potato gave 47.26% higher MEY
- Potato-based systems recorded 19.83% higher yield
- Laser Land Leveling improved yields by 17.7% and reduced irrigations by 50%
- Mulching and residue management significantly improved soil health and moisture retention.
Community Irrigation Success
- Timely transplanted rice achieved:
- Yield: 5208 kg/ha
- Water productivity: 0.786 kg/m³
- Much higher than late-transplanted rice, proving benefits of community-based water management.
Physiological Basis of Improved Abiotic Stress Tolerance
CRA technologies improved the physiological resilience of crops under heat, drought, and flood stresses:
- a) Water Use Efficiency and Root Physiology
- DSR, Zero Tillage, LLL, and Raised Beds improved root length density, enabling greater soil moisture extraction.
- Raised bed planting enhanced aeration, root oxygenation, and deeper rooting, improving drought and waterlogging tolerance.
- Laser Land Leveling optimized soil–water uniformity, reducing physiological drought and heat stress.
- b) Photosynthetic Efficiency and Heat Tolerance
- Timely sowing under zero-till buffered terminal heat stress, maintaining photosynthetic activity and grain filling.
- Mulching and residue retention helped maintain canopy temperature, reduced soil evaporation, and improved stomatal conductance.
- Precision nutrient tools (LCC, NE, Green Seeker) maintained optimal chlorophyll content, increasing photosynthetic capacity under stress.
- c) Improved Nutrient Uptake and Osmotic Adjustment
- Enhanced nutrient management improved nitrogen assimilation, increasing resilience to heat and drought.
- Residue-based systems increased soil organic carbon, enhancing osmotic regulation, water retention, and root-zone nutrient availability.
- d) Molecular and Biochemical Aspects of Stress Tolerance Strengthened
The CRA interventions indirectly promoted molecular and biochemical pathways associated with abiotic stress tolerance:
Practices like DSR, residue retention, and water-efficient irrigation foster:
- Upregulation of HSPs (Heat Shock Proteins) for heat tolerance.
- Activation of aquaporin genes improving cell water transport under drought.
- Expression of N-assimilation genes through precision nutrient management → improved protein synthesis under stress.
-
Agrometeorological Research and Applications
a) Research
- Characterized the agro-climatic resources of Bihar for the assessment of potential agricultural productivity
- Evaluated the agro-climatic onset of the monsoon and delineated water-surplus and water-deficit areas for Bihar
- Contributed significantly to climate change studies and simulation modeling in rice, wheat and maize.
- Developed futuristic model output for winter maize and wheat under increasing temperature regime
- Developed a large number of agroclimatic products/outputs for decision making in agriculture under changing climatic conditions.
- Characterized micro-climate of major crops and evaluated net ecosystem exchange (NEE) over rice-wheat system.
Technological innovations and new products
Concept
- Developed the Concept of climate-smart rice-wheat production system for climatic risk management and higher system productivity
- Successfully developed and implemented community irrigation approach and single-phase 3-hp submersible pump employed in rice-wheat cropping system for climatic risk management
Innovation/ Model
- Decision support system/climate smart irrigation software/App for rice
Products
- Identified critical weather limits for rice, wheat and maize for risk management and developing actional advisories
- Developed 33 Crop Weather Calendars of major crops for generating weather-based advisories, and risk management
- Developed soil moisture index (SMI) and moisture adequacy index (MAI) based LGP products for Bihar
- Developed critical weather thresholds for fall army worm attacks in winter maize
b) Climate Services for the farmers
- Serving farming community with weather-forecast based Agromet Advisories on regular basis for climatic risk management and enhanced farm productivity.
- This service is very popular among farmers because of their reliability and valuable information.
- Large network developed for the continued success of the advisory system. Almost 3,000 framers are availing weather information and advisories on regular basis through WhatsApp.
- Providing micro-level advisory to the farmers under NICRA project. For rice, NICRA farmers gained a net benefit of ₹9,643/acre over non-NICRA farmers.
- Capacity building of farmers and extension agents on climate risk management.
New Innovations Led by RPCAU
The Centre introduced several forward-looking climate innovations:
- Sukhet Model – Monetization of crop residue, household waste & cow dung
- Biochar Production Units – For soil carbon enrichment
- Drainage-cum-Recharge Structures – Enhancing groundwater sustainability
- Strengthened Custom Hiring Centers – Ensuring machinery access
- Aeroponics & Tissue Culture Potato Seed Production – Ensuring high-quality seed supply
Scientific Staff
|
Sl. No. |
Name |
Designation |
Mobile No. |
|
|
1 |
Project Director, CASCC |
9430804115 |
||
|
2 |
Associate Professor, Agrometeorology |
7667349483 |
||
|
3 |
Dr. Ashutosh Singh |
Assistant Professor, Plant Biotechnology |
7892177818 |
|
|
4 |
Dr. Dharani C |
Assistant Professor, Agrometeorology |
9159827365 |

 Users Today : 47
Users Today : 47 Total Users : 4515448
Total Users : 4515448